Abstract
Introduction
Early results of a prospective randomized phase III trial comparing 8 Gy total body irradiation (TBI) and fludarabine (reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC)) against 12 Gy TBI and Cyclophosphamide (standard conditioning (SC)) before allogeneic hemopoietic cell transplantation in patients < 60 years with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in first complete remission (1st CR) had been reported previously (Bornhäuser et al. Lancet Oncology 2012). RIC resulted in a lower incidence of non-relapse mortality (NRM) during the first year after transplantation and comparable overall survival (OS). Based on 10 years of follow-up, we have now performed a 12 months-landmark analysis to compare the incidence of late relapses and overall outcome of the two study arms.
Methods
The retrospective data collection was based on medical reports, phone interviews with the attending transplant physician, the outpatient hematologists, the primary care physicians and the patients themselves. In case of lost to follow-up local registration offices were contacted to obtain information about the survival status. Ninety-nine and 96 patients < 60 years had been randomized to RIC and SC, respectively. RIC consisted of 120 mg/sqm Fludarabine combined with 8 Gy TBI, SC was performed with 12 Gy TBI and 120 mg/kg Cyclophosphamide. Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis consisted of Cyclosporine and Methotrexate on day 1, 3, 6 and 11. Recipients of grafts from unrelated donors (n=78, 40%) received 60 mg/kg antithymocyte globulin. Most patients were transplanted with G-CSF mobilized blood (n=180, 92%). The landmark analysis included patients who were alive, in follow-up, relapse free, with a CR reported prior to the landmark time point of twelve months after transplantation.
Results
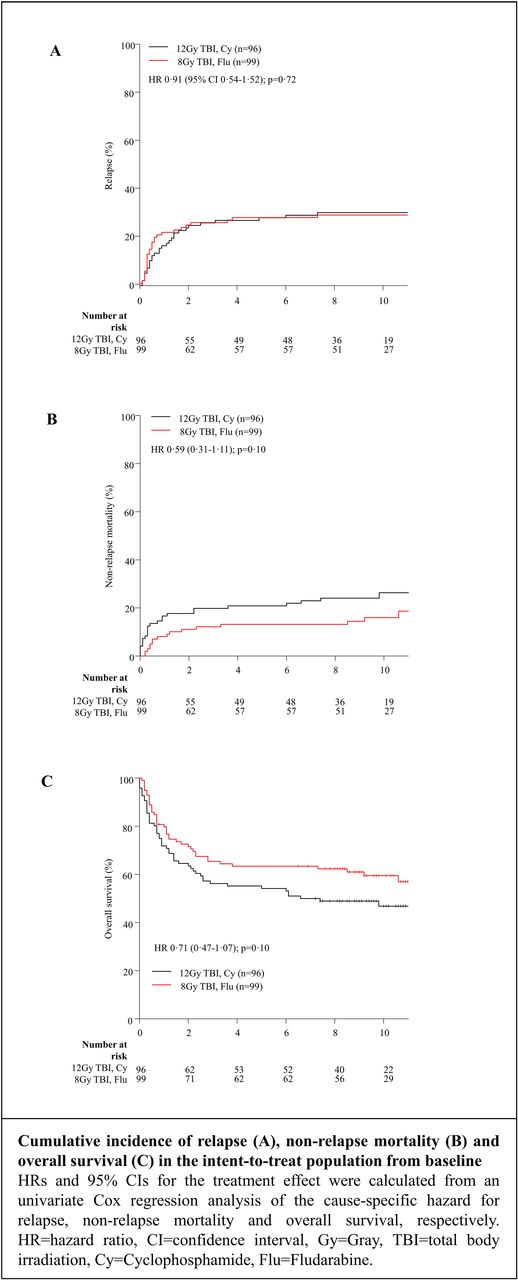
Data collection was performed between January 2016 and June 2017. Median follow-up was 9.9 years (interquartile range 8.5-11.4) from the date of transplantation. Completeness of the follow-up was 99% concerning survival status. The incidence of late relapse in the landmark analysis (cumulative incidence at 10 years) was 10% [95% CI 3-18] for the RIC vs 21% [95% CI 11-31] for the SC arm (HR 0.47 [95% CI 0.19-1.17]; p= 0.11). Interestingly, relapses occurred later in the SC arm than in the RIC arm (median time to relapse 5.0 months (interquartile range 3.0-8.8) in the RIC vs 9.5 months the SC arm (interquartile range 4.5-20.5; p=0.12). However, the cumulative incidence at 10 years from transplantation was almost identical. In the analysis of the patient population from baseline (all patients that were initially included in the study) the trend for a reduced NRM in the RIC arm could still be observed and was statistically significant in patients from 41-60 years (13% [95% CI 5-22] vs 32% [95%CI 19-44] HR 0.43 [95% CI 0.19-0.95]; p=0.036). The probability of OS at 10 years was 60% [95% CI 50-70] in the RIC arm and 47% [95% CI 38-59] in the SC arm with a HR of 0.71 (0.47-1.07); p=0.10), respectively. The probability of disease free survival at 10 years was 55% [95% CI 45-66] in the RIC arm vs 43% [95% CI 34-55] in the SC arm (HR 0.76 [0.51-1.14]; p=0.19), respectively. The incidence of chronic GVHD at five years (42% vs 48%), rates of secondary malignancies (4% versus 7%) and rates of late complications did not differ significantly between the RIC and the SC arm.
Conclusion
RIC with 8 Gy TBI and Fludarabine does not increase the risk of late relapse compared to SC after allogeneic transplantation in patients with AML in 1st CR. Given the significantly lower early morbidity and toxicity, RIC with moderately reduced doses of TBI or alkylating agents can be regarded as optimized conditioning strategy in AML patients < 60 years transplanted in 1st CR.
Schetelig: Sanofi Aventis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria. Hegenbart: Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Prothena: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Dreger: Riemser: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Travel grants, Speakers Bureau; Jansen: Consultancy; Riemser: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Travel grants, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Riemser: Consultancy, Research Funding; Riemser: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Riemser: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Travel grants, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Travel grants, Speakers Bureau; Jansen: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Travel grants, Speakers Bureau; Riemser: Consultancy, Research Funding; Riemser: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Travel grants, Speakers Bureau; Jansen: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Travel grants, Speakers Bureau; Jansen: Consultancy; Riemser: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Travel grants, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Jansen: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Travel grants, Speakers Bureau; Jansen: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Jansen: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; medac: Other: Travel grants; Jansen: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; medac: Other: Travel grants; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; medac: Other: Travel grants; medac: Other: Travel grants; medac: Other: Travel grants; medac: Other; medac: Other; medac: Other; medac: Other; medac: Other: Travel grants; Jansen: Consultancy; Riemser: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Jansen: Consultancy; Jansen: Consultancy; Jansen: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Travel grants, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Travel grants, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Travel grants, Speakers Bureau; Riemser: Consultancy, Research Funding; Riemser: Consultancy, Research Funding; Riemser: Consultancy, Research Funding. Siepmann: European Academy of Neurology: Research Funding; Michael J. Fox Foundation: Research Funding; Prothena and the German Parkinson's Disease Association (DPG): Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal